|
Updated on:
|
CleanIE
Background When you use IE, like with most Web browsers, a lot of information about is captured onto the hard drive of the computer you are using, like your name, e-mail address, Web sites you've visited, and so on. All this information is stored in files called "cookies" and in folders called "cache".
Cookie The name cookie is derived from UNIX objects called "magic cookies". These are tokens that are attached to a user or program and change depending on the areas entered by the user or program. Cookies are also sometimes called persistent cookies because they typically stay in the browser for long periods of time.
Cache Since all this information is being written to your hard drive, it is taking up drive space. Depending on your browser settings, the cache could eventually megabytes of information, possibly resulting in a potential slowdown in your browser activity. In addition, Web sites might appear to not have any new information on them because the browser is pulling the information from the cache rather than Web site.
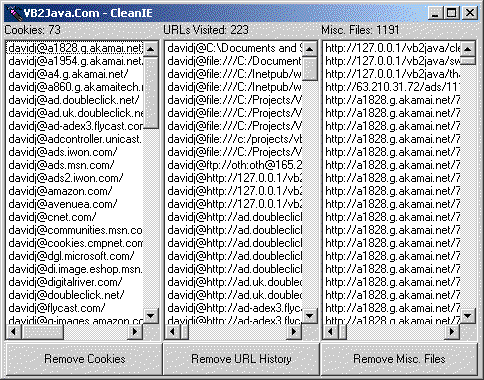
Purpose of CleanIE CleanIE is primarily designed for people who use public or shared computers, like the computer at the library or pressroom at Comdex, or even a shared computer at work. It can run as either a command-line application or as a Windows application. As a command-line application, all the cookies, cache and typed URLs will be purged from the computer system based on who's logged into the computer. In other words, it will only purge the information of the person who's currently logged into the computer and not touch anyone else information. The reason for being able to run it from a command-line is so you can keep it on a floppy disk and run it when you need to. However, the one caveat is that you will need the MSVBVM60.DLL installed on the computer or on the floppy disk. To run CleanIE as a command-line application, go to the folder where CleanIE resides and type the following at a DOS prompt: CLEANIE /C Once completed, a dialog box will thank you for using CleanIE. You can also create a shortcut to do that same thing. As a Windows application, you will see three list boxes: Cookies, URLs you've visited, and cached file URLs. You can select one or all the files from a list for removal. If you double-click on an item in the "URLs Visited" or "Misc Files" columns, your default browser will launch and you will be taken to URL, assuming you have an active connection to the Internet.
System Requirements This program is freeware/donationware. You are free to use this program on as many computers as you want without the worry that the software police will come knocking on your door for a registration fee. We do ask that if you feel so inclined, feel free to make a donation to our software development cause.
|